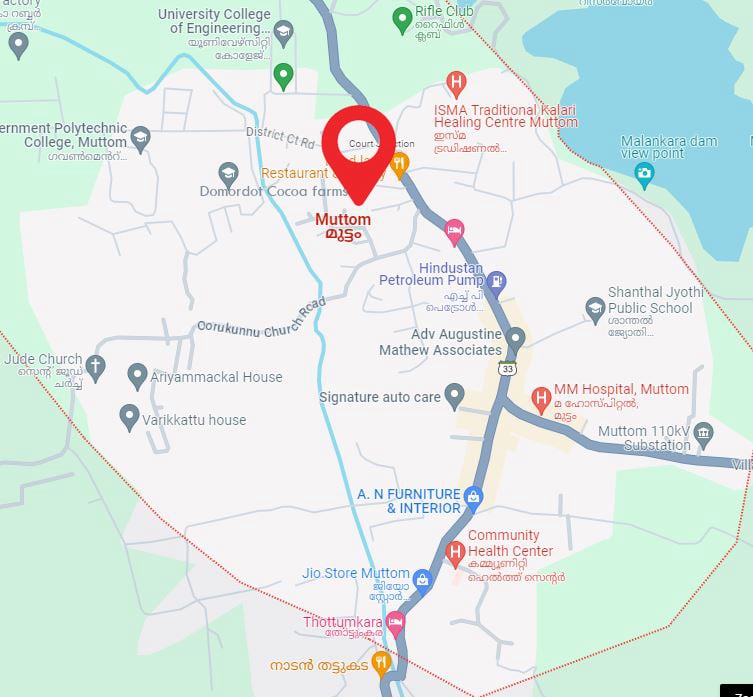
Domordot Cocoa Farms
Domordot cocoa farms are located in Idukki, Kerala, India! Nestled in the lush green landscapes of the Western Ghats, our cocoa plantations offer a unique and immersive experience for chocolate enthusiasts, nature lovers, and curious minds alike.
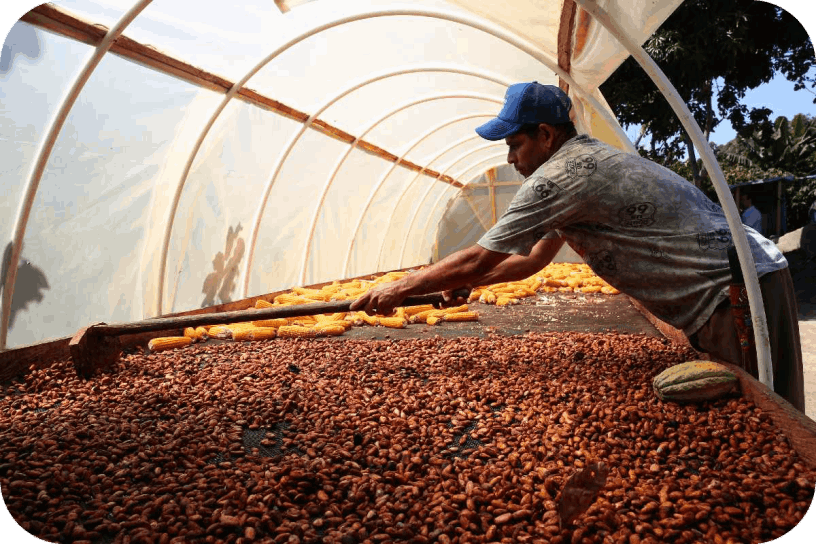
Explore the rich heritage of cocoa cultivation in Idukki, where traditional farming practices seamlessly blend with the serene beauty of the region. Domordot is a gateway to the fascinating journey of cocoa from bean to bar, showcasing the meticulous process that transforms these humble beans into the delectable chocolate we all love.
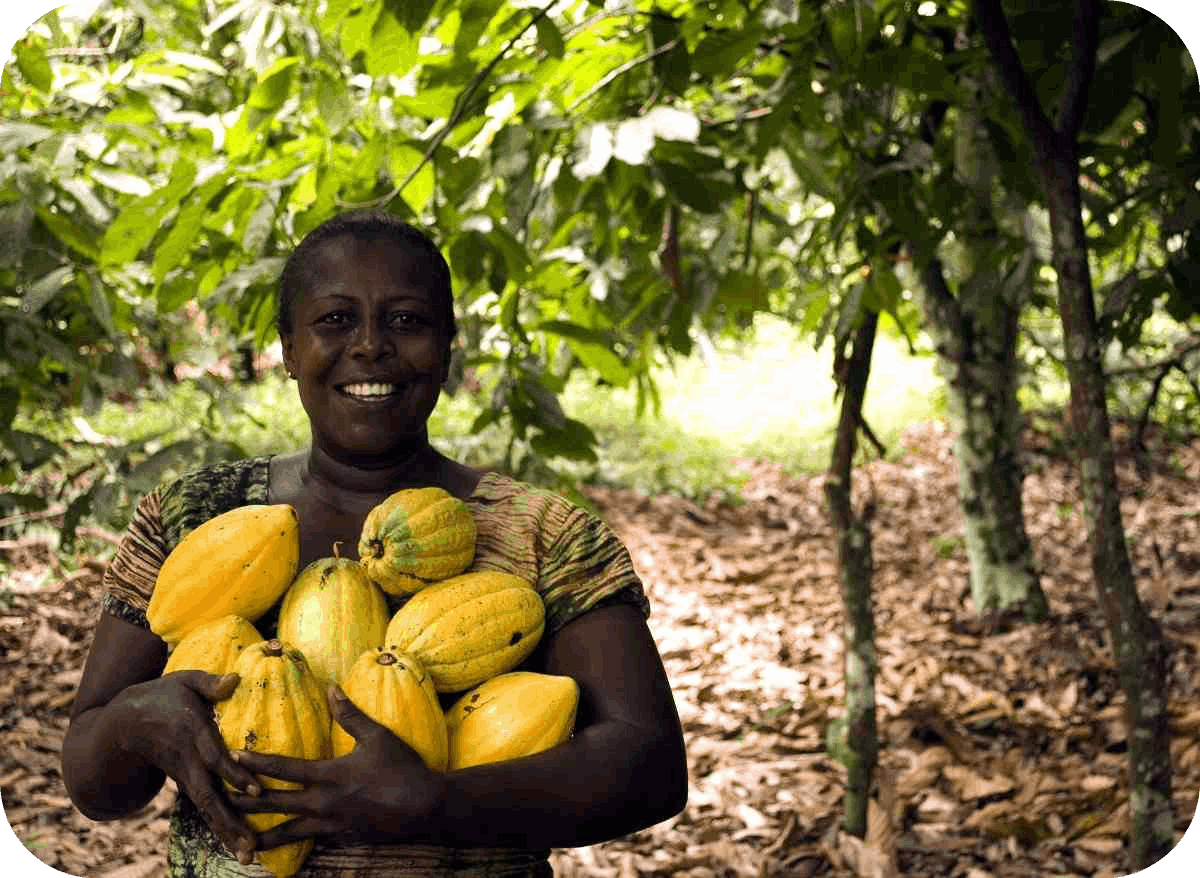
Discover the secrets of sustainable farming as you delve into the stories of local farmers who have perfected the art of cultivating cocoa in harmony with nature. From nurturing the cocoa trees to harvesting the pods, our website provides a virtual tour of the entire cultivation process, giving you a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship behind every cocoa bean.
Immerse yourself in the breathtaking landscapes of Idukki, where cocoa farms coexist with the diverse flora and fauna of the region. Our photo galleries capture the essence of the farm life, showcasing the vibrant colors of cocoa pods against the backdrop of the verdant hills. Learn about the unique microclimate of Idukki that contributes to the exceptional flavor profile of the cocoa grown here.
Whether you're a connoisseur seeking to deepen your knowledge of cocoa cultivation or a traveler yearning for a virtual escape to the idyllic landscapes of Idukki,